There are some excellent SEO tools for a variety of uses. With these tools, you can check backlinks, perform keyword analysis, find mentions of your brand and article ideas, and even conduct complex SEO audits. However, whether you're an agency, a small business, or a large corporation, these tools won't cover all your needs. The Search Console helps fill in those gaps.
If you're not familiar with this tool, we invite you to check out this GSC tutorial for beginners before continuing to read.
If you're doing SEO optimizations yourself, then you'll frequently use the Search Console and other tools. Not entirely comfortable with the Search Console? Don't worry. Today, I'll teach you how to use the main features of the Search Console.
Since 2019, the enhanced Search Console has been an exceptional tool that you can't do without for tracking your website's SEO and identifying the main improvements to make to enhance your SEO. Let's look at seven steps to use the new Search Console effectively and the differences between the old and new versions of the GSC.
Let's get started!
🚀 Quick read: How to use Google Search Console in 7 steps?
- Install GSC on your website;
- Define your domain name;
- Link Google Analytics;
- Add your sitemap;
- Use the coverage report;
- Update your content;
- Boost the pages of your choice.
1️⃣ Step 1. Add and verify your website
Before you can take advantage of the Search Console's features, you must, of course, add and verify your website. Open the drop-down menu at the top left of your dashboard and select "Add a property."
To "validate the property," please refer to our comprehensive article that explains step by step how to install Google Search Console.
2️⃣ Step 2: Set a preferred domain
By setting a preferred domain, you tell Google which version of your URL you want to display in search results (https://www.example.com or https://example.com). Choosing one or the other will not give you any SEO advantage.
Select your property on the Search Console homepage. Then click on the gear icon at the top right of your dashboard and select "Site Settings."
In the "Preferred Domain" section, you'll see the option to choose between www.example.com and example.com. There's also an option for "Do not set a preferred domain." If you select this option, Google may treat the www and non-www versions of the domain as separate references to distinct pages. This could negatively impact link juice and organic search visibility. By choosing a preferred domain, you're asking Google to treat all domains the same way.
3️⃣ Step 3: Link Google Analytics to Google Search Console
Google Analytics provides you with general data on traffic and conversions, while the Search Console gives you an overview of the factors behind this data. Connecting the two tools will allow you to get more value from the reports.
To link Google Analytics to your Google Search Console account, click the "Administration" button at the bottom of the Google Analytics homepage. In the PROPERTY column, click on "Property Settings."
If you don't have access to Property Settings, it means you're not authorized to make changes. In this case, you'll need to obtain permission from another owner.
Scroll down to Search Console Settings. Your website's URL should appear, confirming that it's validated in the Search Console and that you're authorized to make changes. In the Search Console section, select the report views in which you want to display Search Console data.
You'll now see a Search Console report in the "Visitors" tab of your Google Analytics dashboard. With this report, you can now verify that pre-click data (queries, impressions) matches post-click data (bounce rate, goals achieved). The landing page report contains search data for each URL on your website that appears in search results. You can use this report to check the effect of changes on traffic. This involves analyzing the cause-and-effect links between updates or changes in settings on content performance.
For example, you can learn more about the evolution of click-through rates over time. Or, find out how the average position of content on a search result page affects the average time spent on the page. Linking the Search Console and Google Analytics allows you to analyze all these unique relationships between SEO factors. You can also use the reports on countries, devices, and queries to analyze these same relationships based on countries, devices, and search queries.
Unfortunately, the Search Console will only start collecting data on your site from the moment it's installed. The new Search Console offers 16 months of data compared to 3 months for the old Search Console. If you've just connected Google Analytics to the Search Console, you'll have to wait before you can take advantage of this improvement.
4️⃣ Step 4: Add a sitemap
Not sure if you have a sitemap? Check if your site has a sitemap by typing "https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml". Be sure to replace "example" with your domain name. If nothing appears, then your site doesn't have a sitemap. Of course, you must have a sitemap if you want to submit one to the Search Console.
Here are some sitemap best practices:
- File size: Less than 50 MB
- Number of URLs: 50,000
- If you have more than 50,000 URLs: split your sitemaps
- Include only canonical URLs. It's essential to exclude URLs that you've blocked in the robots.txt file
- Here's what Google says: "XML sitemaps should contain the URLs of all the web pages on your site." If you have a large website, understand "all the important web pages on your site." This includes any web page with unique, high-quality content. This excludes "utility pages," i.e., web pages that might be useful to a user but are not useful as a landing page for a search.
- Common CMS (Content Management Systems) like WordPress and Drupal have plugins that help you generate sitemaps. Some, like Squarespace, generate and update them automatically.
- If all else fails, this article explains how to create a dynamic sitemap. If you have a small website, this tool will create it for you.
So, you should have your sitemap! To help Google understand your website's content, you'll submit it. To do this, go to the sitemap tab in the new Search Console. Enter the URL of your new sitemap, click "Submit," and you're done!
5️⃣ Step 5: Use the index coverage report to fix errors
In the new Search Console, this report is available from the dashboard. In the old Search Console, the report was called "index report."
According to Google, the new report provides the same information as the old one, as well as detailed information on indexing status. What kind of conclusions can you draw from this new report? Let's go through each tab.
- Error: Review all potential website errors to fix them. These can include server errors, redirect errors, robots.txt file code errors, and many more.
- Pages with warnings: Pages with warnings are indexed but blocked by the robots.txt file. Note that Google prefers the Meta noindex tag to the Disallow: directive in the robots.txt file. Indeed, a web page blocked by the robots.txt file can still be indexed if other pages link to it. These warnings give you the opportunity to crawl and correctly deindex these web pages.
- Valid pages: All these pages have been indexed. If you see the message "Indexed, but not submitted via a sitemap," make sure to add this URL to your sitemap. The message "Indexed, duplicate page without user-selected canonical URL" means that the web page has duplicates, none of which are marked as canonical.
- Excluded pages: These are web pages that have been blocked by a "noindex" directive, a web page removal tool, the robots.txt file, or a crawl anomaly (duplicate content, etc.).
Google provides a good overview of the meaning of each of these statuses and how to fix them. We don't have time to cover all the details today, but in general, you can get the 411 on each URL by clicking on the tab you want to examine, then clicking on the description in the "Details" section. Click on the URL in the "Examples" tab. This will open a panel that will give you some clues to investigate the issue.
Here's what you can do to fix errors:
- Inspect a live URL (URL Inspection Tool): Check the page, its last crawl time, whether crawling is allowed or not, whether indexing is allowed or not, whether you've declared this page as canonical or not, and whether Google considers this page canonical or not.
- Block the robots.txt file: Open your website's robots.txt file (example.com/robots.txt) and check which elements are blocked. You can use the robots.txt testing tool that will highlight the blocked parts of the pages for you.
- View the crawled page (URL Inspection Tool): This tool allows you to see the page as it appears to Googlebot. It shows you the HTTP response headers it receives when viewing the page. Click on "View the crawled page" to get a screenshot showing the physical layout of your web page.
- See the URL in a SERP: Allows you to see what your web page looks like in the SERP.
This feature is available for all your URLs. You can use it to check the statuses associated with errors, warnings, etc. Be sure to validate your corrections so that Google reindexes the affected web page. That's all for the index coverage report. It can be used to detect and correct any errors associated with your website.
6️⃣ Step 6: Use the performance report effectively to update content
All the settings you see in Google Analytics after connecting your accounts come from the performance report. This report replaces the "Search Analysis" report in the old Search Console. The two reports are very similar. Let's see how to make the most of this report.
First, open the performance report. It's the first report displayed in your overview. You're not limited to tracking these metrics in Google Analytics: you can also use them to search for performance improvement opportunities. The best way to do this is to use the filter to analyze data based on queries, web pages, countries, or device types. You can choose to display, for example, web pages that appear in search results with a click-through rate (CTR) lower than the website's average.
You can also view queries for which you're not in the top 10 but still get good impressions. This allows you to identify your weaknesses and strengths and optimize web pages to try to boost your ranking. Most third-party SEO tools have similar features that let you search for keyword opportunities, but it's much more convenient to get this type of data directly from Google!
Also, look at issues related to the mobile version of your site. As you probably know, mobile users now make up the majority on Google. In fact, the search engine now primarily crawls your site on their mobile version. By respecting the information provided in their own tool, you have a great opportunity to improve your ranking in the SERP.
7️⃣ Step 7: Use the link report to boost specific pages
The link report is located at the bottom of your dashboard. It has many applications. Here are my two favorites:
- Boost specific web pages by using your web pages that generate the most backlinks. Linking the web pages you want to boost with the pages that have many links is an excellent way to increase your ranking. To identify the pages with the most link juice (or "link juice" in French) on your website, click on "Top landing pages" under "External links." You can sort the results by the number of referring domains, an important ranking factor for Google. Find the web pages that are about to generate significant business value and create internal links to these web pages.
- Disavow inbound links. Go to the "Top source sites" section in the link report overview. Select a URL from the list to see all the sites linking to that page. Check if any sites seem to be of poor quality and use Google's inbound link disavowal tool to refute them. Caution: According to Google, you should only refute links if you're sure they're harming your website. Refuting links that improve your performance will harm your website. However, it's essential to check if dubious domains are pointing to your website.
💫 Going further
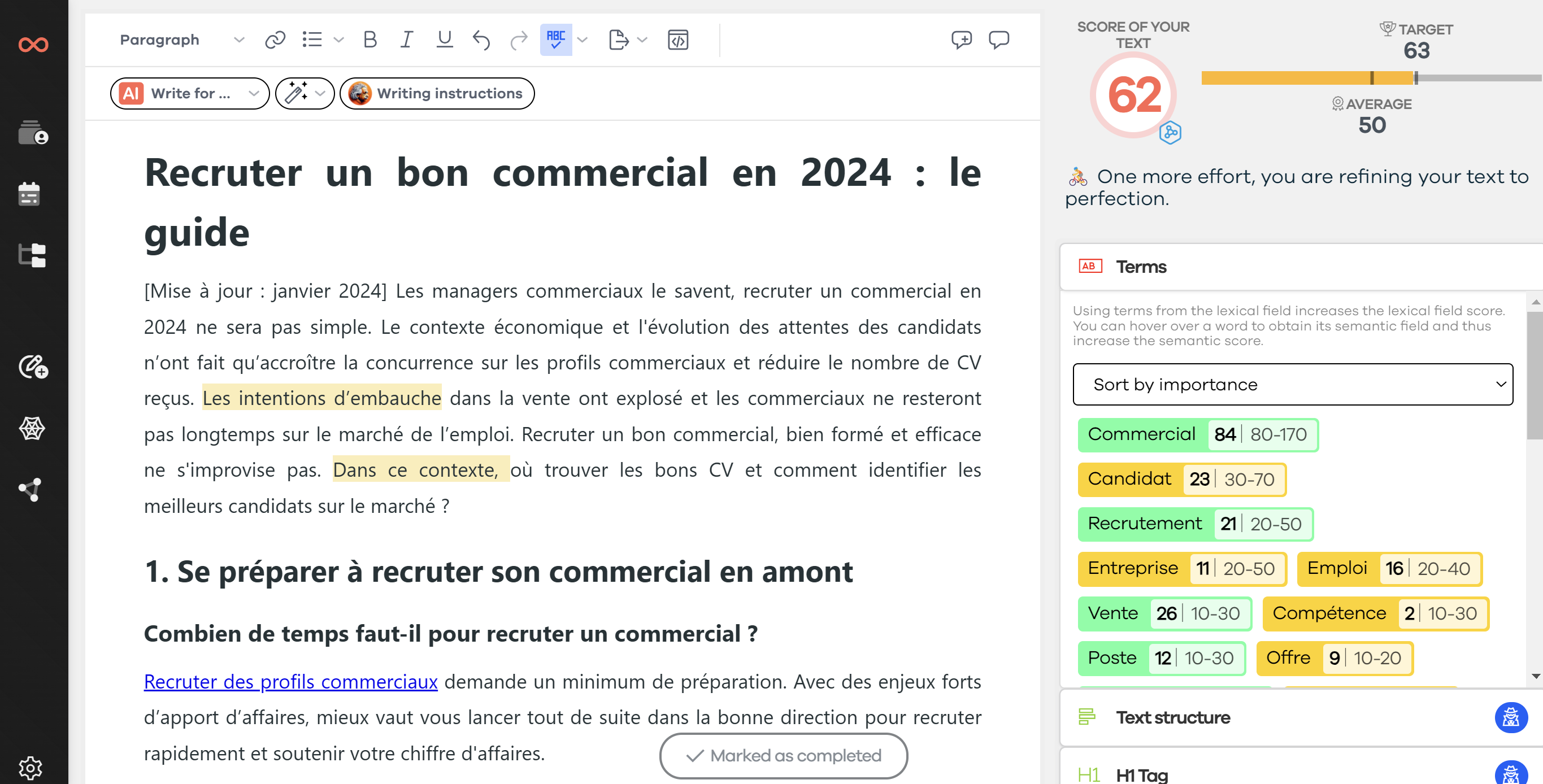
If you've followed these 7 steps, you're able to use the Search Console effectively. These concepts and reports are the most useful. That said, you can, of course, go further. Since last September, SEOQuantum has integrated Google Search Console into its tool. Access all your Search Console data in just a few clicks from the tool. A real innovation that should make your life easier.
A comprehensive analysis is done via Search Console, allowing you to find the details of each of your pages in a simplified way, without settings, without searching. Everything is at your fingertips in just a few clicks.
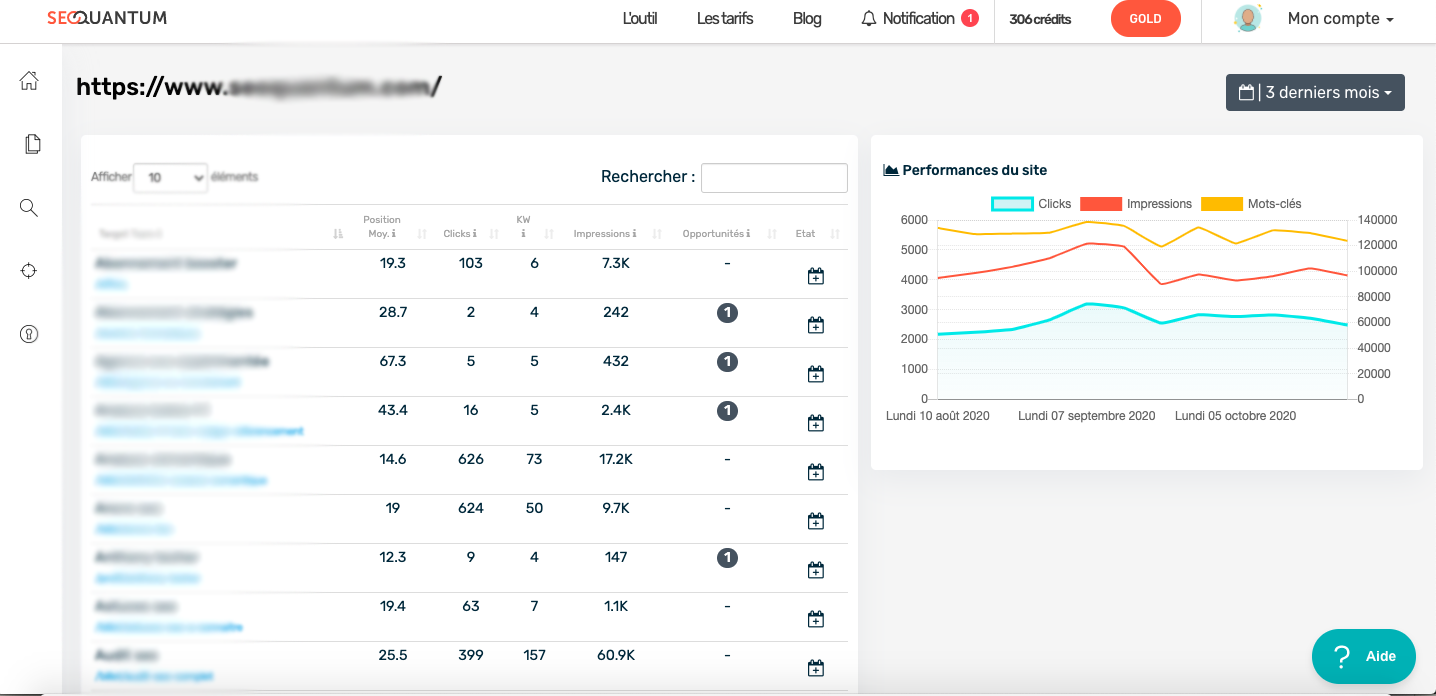
The tool will group keywords that generated the most traffic on the ranked page by cluster. If you click on the keyword in question, you'll get the complete list of associated words. You can also directly launch a semantic analysis from this page.
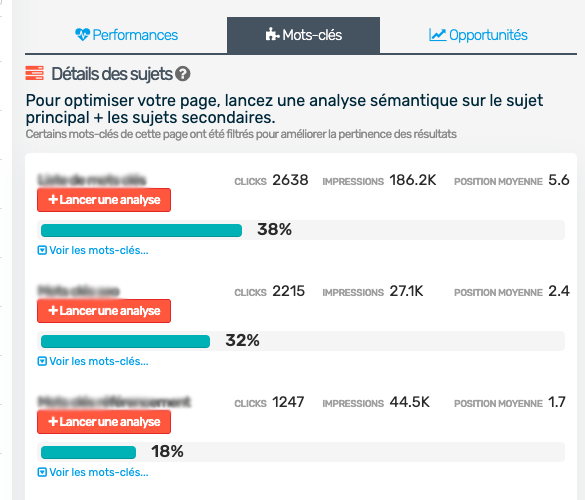
The tool also offers an opportunity tab, allowing you to see what you could do to drive more traffic (e.g., change your tag and meta description, add keywords...). In short, as you can see, everything is now just a few clicks away.
Visit our YouTube page to discover how to connect SEOQuantum and Search Console.
In previous articles, we offered a Google Search Console guide and some tools for installation. But the big innovation we're offering is the integration of Search Console within SEOQuantum to easily track the performance of your content optimizations, which I just mentioned.
For those who have already tested it, what did you think? And if you haven't done it yet, it's your turn! You're just one step away from being able to optimize content that will bring you good SEO traffic and a better conversion rate!
🙏 Sources used to write this article
Need to go further?
If you need to delve deeper into the topic, the editorial team recommends the following 5 contents: