Today, it's hard not to have heard of RankBrain. This new system from Google, along with its impact on search results, raises many questions within the SEO community.
Through this 3rd installment of the SEOQuantum semantic guide, we will try to understand how RankBrain works and if there's anything we could do to optimize content.
What is Google RankBrain?
Google Rank Brain is a machine learning system (based on deep learning) developed by Google to improve the relevance of search results. It allows for interpreting new queries that have not been previously searched.
Some SEO experts consider that RankBrain is part of the Hummingbird search algorithm (Google Hummingbird), announced in 2013, to help the search engine better understand the meaning of the query, especially those composed of several words.
The first official statement of Google RankBrain was made by Greg Corrado in October 2015. Greg stated that, shortly after deployment, RankBrain became the third most important "factor" in search ranking.
Given the impact, it is important to understand exactly how the algorithm works, and what it will bring to internet users, but also its impact on SEOs.
How does Google RankBrain work?
As mentioned above, the main purpose of RankBrain is to provide more relevant results by interpreting the meaning of entire sentences rather than focusing on keywords. One facet of this algorithm is the assimilation of content (this article will only deal with this aspect).
Rankbrain effectively manages long-tail queries as well as their similarities between them (how are they connected? to which particular topics?).
Thanks to this, Google can understand a sentence that has never been processed before, by correlating it (via similarity) to already known sentences/concepts.
As a machine learning system, RankBrain is constantly learning, paying particular attention to parameters such as pogosticking, bounce rate, or time spent on a page. If a user considers the displayed results unrelated to the search, next time, the algorithm will display other results for this query.
What are the implications for Google users?
- You will be able to find information on a concept or event without using that particular word ("What is the animal at the top of the food chain?")
- You will get more relevant results for ambiguous searches that have multiple meanings (for example, "Jaguar" as the car brand or "jaguar" as the animal)
- If you perform a search that Google has never encountered before, it will be correctly interpreted and adapted to the most known vector
Google does not disclose the exact algorithms it uses, but we know that its operating principles are close to word embedding.
The Word embedding approach
Choosing a good word analysis method is often essential to successfully carry out content optimization tasks. The frequency representation of words is the most commonly used (see the notion of WORDPRINT in our SEOQuantum tool). However, this representation has the defect of capturing little information about the context of the word and their relationship with each other.
Since the late 2000s, techniques based on artificial neural networks have emerged (deep learning). This is Word embedding.
Within a corpus, a word is not used in any way, it is contextualized: in relation to other words. This approach allows representing a word by a vector depending on its position in the corpus. Word Embedding methods build a context window for each word. We use context vectors to represent each word through a matrix. Words with similar meanings are located near the terms of the vector space.
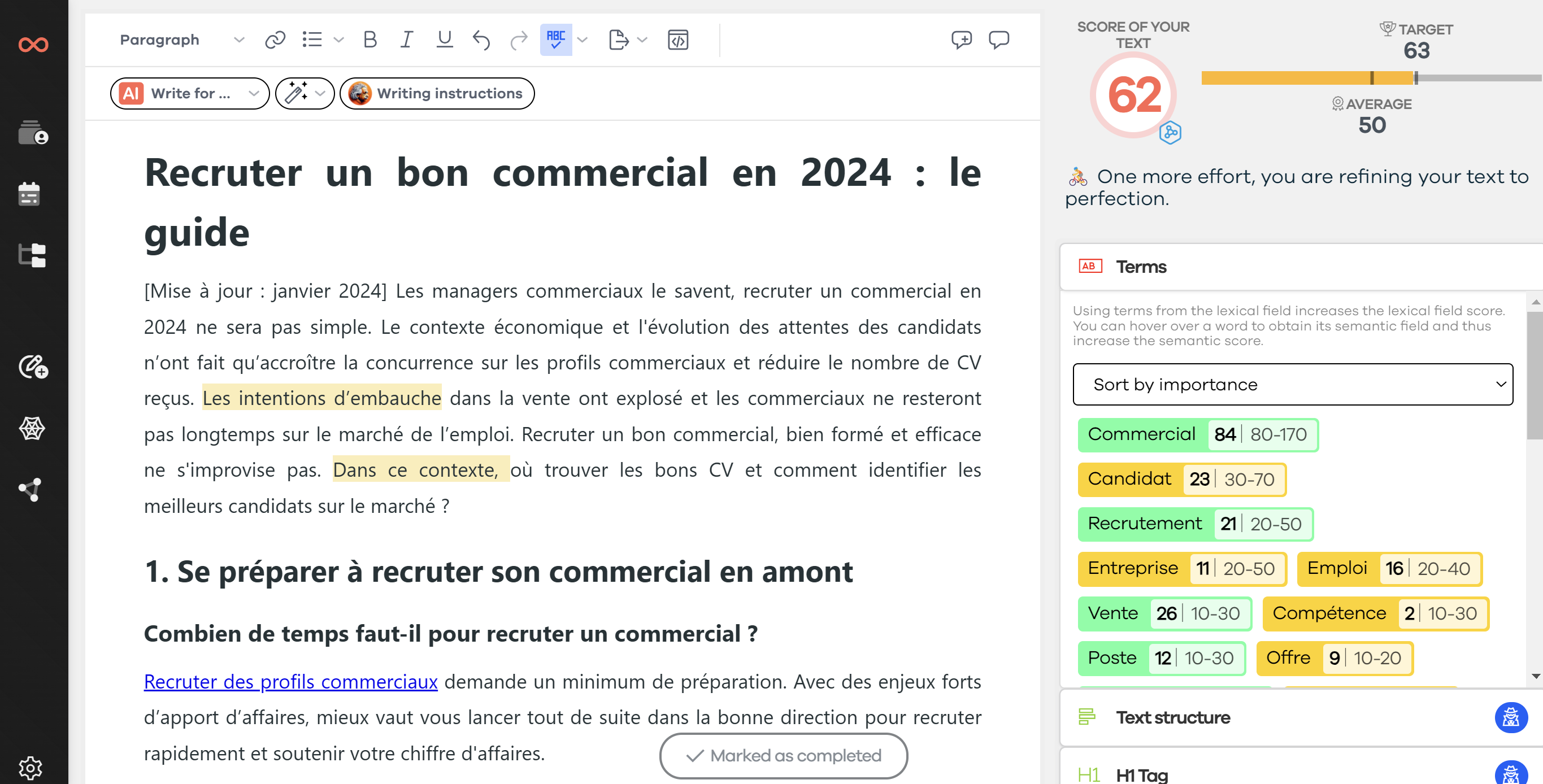
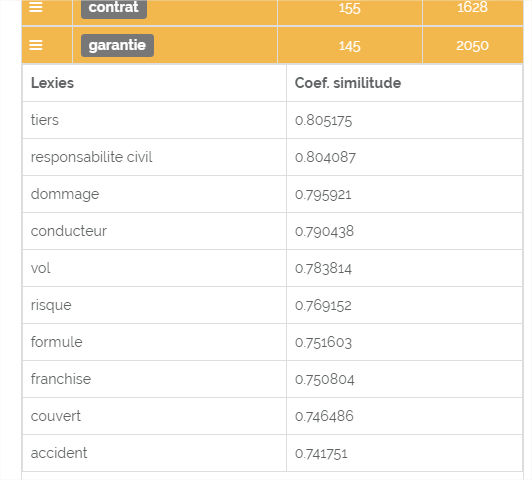
Here is an example in SEOQuantum of the lexies closest to "guarantee" for the query "insurance comparator"
The SEOQuantum tool approach
We wanted to have a better understanding of how RankBrain works and, for this purpose, we created our own SEOQuantum semantic analysis tool.
We created similarity links between lexies using a deep learning algorithm. For each of your queries on SEOQuantum, we process text corpora to extract the vectors of each of the words.
In the end, these are not exactly "synonyms" or "associated keywords" (words returning similar results in the SERP) or co-occurrences, but something very different.
With SEOQuantum, we tried to understand the way Google "thinks" and the words it considers related to your targeted keywords.
Test it and you will see that the results are quite interesting and sometimes unpredictable. Sometimes, the words that we closely associate with a certain concept are not those that appear near it in the text, for example for the lexie "SEO" for the query "seo agency":
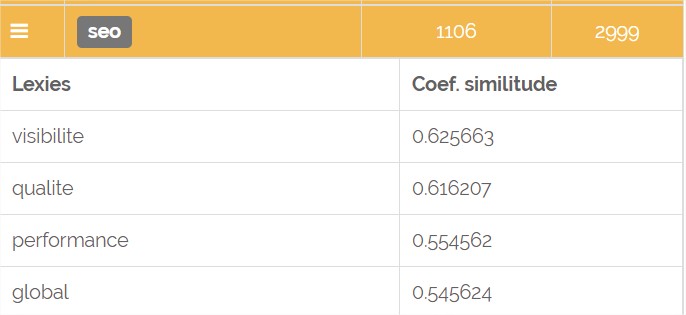
> Here, we can see that the lexie SEO (for the query "seo agency") is associated with the concept of "visibility", "quality" and "performance"... food for thought :-)
How to optimize RankBrain?
According to Google, there is no way to optimize RankBrain. RankBrain does not have a notable impact on search results, as its primary goal is to handle queries that lack relevance.
The fact is that it is impossible for an SEO to ignore the existence of the algorithm in your natural referencing actions. So, what do we do?
Develop your keyword list beyond synonyms and co-occurrences:
No longer create pages or content tailored to a single keyword. For maximum effect, try to think "semantic universe" from now on:
- Group your targeted keywords, as well as their variations and associated searches
- Use additional lexies that appear the same semantic concept (use the similarity coefficient of our SEOQuantum tool)
Focus on creating high-value content
- Be loquacious, seek to cover all aspects of the subject, answer as many questions as you can.
The goal of Google and RankBrain in particular is to provide users with the most useful and relevant results. If you share this same goal, you are more likely to succeed.
Optimize your content for your audience and not for search engines
- Be natural: although this statement may seem banal, it is particularly true in the context of deep learning. Remember that the algorithm learns from human behavior.
If people appreciate your content and consider it relevant, Rankbrain will naturally consider it the same.
The world of SEO is constantly evolving. The emergence of "deep learning" and word embedding have significant consequences in our work as SEOs. It is difficult to optimize for Rankbrain without the use of deep learning tools.
The RankBrain system is constantly improving through machine learning: its goal is to offer the best content to the user. All you have to do is make sure your content is as relevant and complete as possible.
### And you?
And you, what is your experience with Rankbrain? Leave a comment to share your recommendations!
Need to go further?
If you need to delve deeper into the topic, the editorial team recommends the following 5 contents: